Author Bio: Dr. Ram Prakasha BPTh
Written by a Physiotherapy and Public Health professional with experience in neurological rehabilitation and health awareness. The content is intended for educational purposes only.
What Is Bronchitis?
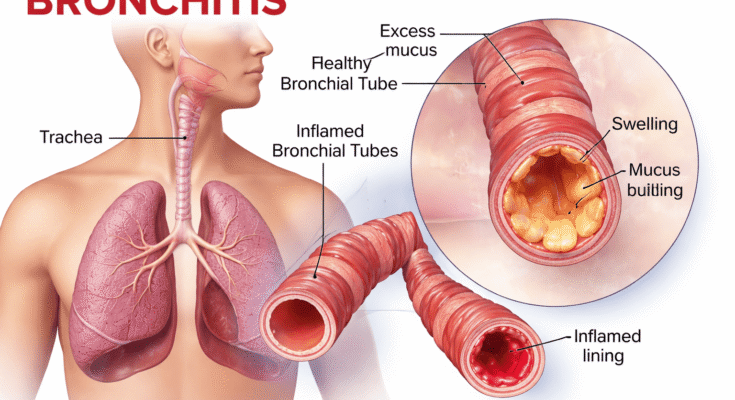
Bronchitis: Causes Symptoms Bronchitis is the inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from the lungs. Because these tubes swell, airflow becomes restricted. Consequently, patients experience coughing, chest discomfort, and breathing difficulty.
Additionally, bronchitis can be short-term or long-lasting. Therefore, medical experts divide it into two main types: acute bronchitis and chronic bronchitis.
Types of Bronchitis
1. Acute Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis usually develops suddenly. Most often, it follows a viral infection like the common cold or flu. Fortunately, acute bronchitis typically resolves within 1–3 weeks.
Furthermore, acute bronchitis is highly common during winter seasons. Since viruses spread easily, respiratory infections increase during cold months.
2. Chronic Bronchitis
Bronchitis: Causes Symptoms Chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition. In fact, it is considered a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). For diagnosis, a productive cough must last at least three months for two consecutive years.
Importantly, smoking is the leading cause of chronic bronchitis. Therefore, lifestyle choices play a major role in disease progression.
Causes of Bronchitis
Bronchitis develops due to various factors. Most commonly, infections and irritants trigger airway inflammation.
Common Causes Include:
- Viral infections
- Bacterial infections
- Cigarette smoking
- Air pollution
- Chemical fumes
- Dust exposure
- Weak immune system
As a result, the bronchial lining becomes irritated, swollen, and filled with mucus.
Symptoms of Bronchitis
Bronchitis symptoms vary depending on severity and type. However, some symptoms remain common in most cases.
Typical Bronchitis Symptoms
- Persistent cough
- Thick mucus (clear, yellow, or green)
- Chest tightness
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Mild fever and chills
- Wheezing
Additionally, chronic bronchitis symptoms are usually more severe and long-lasting. Therefore, early detection is crucial.
Risk Factors for Bronchitis
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing bronchitis. Because these risks are avoidable, prevention becomes possible.
Major Risk Factors
- Smoking or passive smoking
- Repeated respiratory infections
- Occupational exposure to dust or chemicals
- Poor air quality
- Asthma or allergies
- Low immunity
Consequently, lifestyle modification significantly reduces bronchitis risk.
How Bronchitis Is Diagnosed
Bronchitis: Causes Symptoms Diagnosis begins with a clinical examination. Initially, doctors evaluate symptoms and medical history. Then, further tests may be advised.
Diagnostic Methods
- Physical examination
- Chest X-ray
- Sputum test
- Pulmonary function test
- Oxygen level measurement
Therefore, accurate diagnosis helps determine the correct treatment plan.
Treatment for Bronchitis
Bronchitis treatment depends on whether the condition is acute or chronic. In most cases, treatment focuses on symptom relief and airway healing.
Medical Treatment Options
- Bronchodilators
- Cough suppressants
- Expectorants
- Anti-inflammatory medicines
- Antibiotics (only for bacterial infection)
- Oxygen therapy (severe cases)
Importantly, antibiotics are not useful for viral bronchitis. Thus, misuse should be avoided.
Home Remedies for Bronchitis
Home care plays a vital role in bronchitis recovery. Along with medication, natural remedies support healing.
Effective Home Remedies
- Warm fluids and herbal tea
- Steam inhalation
- Honey for cough relief
- Ginger and turmeric
- Adequate rest
- Humidified air
As a result, symptoms reduce faster and comfort improves.
Diet and Nutrition in Bronchitis
Nutrition supports immune strength. Therefore, diet plays a key role during bronchitis recovery.
Recommended Foods
- Fruits rich in vitamin C
- Warm soups and broths
- Garlic and onion
- Lean proteins
- Plenty of water
Meanwhile, avoiding cold drinks, fried food, and smoking accelerates healing.
Bronchitis in Children
Bronchitis in children often develops after viral infections. Because children have smaller airways, symptoms may appear severe.
Warning Signs in Children
- Fast breathing
- Continuous coughing
- Poor feeding
- Bluish lips
- High fever
Hence, medical attention is required if symptoms worsen.
Complications of Untreated Bronchitis
If bronchitis is ignored, complications may occur. In some cases, it can become life-threatening.
Possible Complications
- Pneumonia
- Chronic lung disease
- Reduced lung function
- Respiratory failure
Thus, early treatment prevents long-term damage.
Prevention of Bronchitis
Prevention is always better than cure. Thankfully, bronchitis can be prevented through simple measures.
Preventive Tips
- Quit smoking
- Avoid polluted environments
- Use masks in dusty areas
- Practice good hand hygiene
- Take flu vaccination
- Strengthen immunity
Consequently, respiratory health remains protected.
When to See a Doctor
Medical help should be sought if symptoms persist. In particular, chronic cough requires evaluation.
Consult a Doctor If:
- Cough lasts more than 3 weeks
- Breathing becomes difficult
- Blood appears in sputum
- Fever remains high
- Chest pain increases
Therefore, timely care ensures better outcomes.
Living With Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis requires long-term management. However, quality of life can still be maintained.
Management Strategies
- Smoking cessation
- Pulmonary rehabilitation
- Regular exercise
- Medication adherence
- Air quality control
Over time, symptoms can be controlled effectively.
FAQs About Bronchitis
1. Is bronchitis contagious?
Yes, acute bronchitis caused by viruses can be contagious. However, chronic bronchitis is not infectious.
2. How long does bronchitis last?
Acute bronchitis lasts 1–3 weeks, whereas chronic bronchitis lasts for months or years.
3. Can bronchitis heal without medicine?
Yes, mild bronchitis can heal with rest, fluids, and home remedies.
4. Is bronchitis serious?
Usually not, but untreated bronchitis may lead to complications.
5. Can exercise help bronchitis?
Yes, light breathing exercises improve lung function in chronic cases.
6. Is bronchitis the same as asthma?
No, bronchitis and asthma are different, though symptoms may overlap.
7. Can children get bronchitis repeatedly?
Yes, especially if they have weak immunity or frequent infections.
Conclusion
Bronchitis: Causes Symptoms Bronchitis is a common yet manageable respiratory condition. With early diagnosis, proper treatment, and lifestyle changes, recovery is achievable. Most importantly, avoiding smoking and improving immunity significantly reduce risk.
Therefore, understanding bronchitis empowers individuals to take control of their respiratory health. Ultimately, awareness, prevention, and timely care ensure a healthier life.
Treatment of Bronchitis: A Physiotherapy Perspective
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the treatment and long-term management of bronchitis. While medicines reduce inflammation and infection, physiotherapy focuses on improving lung function, clearing secretions, and enhancing breathing efficiency. Therefore, a physiotherapy-based approach is especially valuable in chronic bronchitis and recurrent cases.
Why Physiotherapy Is Important in Bronchitis
In bronchitis, excess mucus accumulates inside the bronchial tubes. As a result, airflow becomes restricted and oxygen exchange reduces. Physiotherapy techniques, however, help mobilize and remove these secretions. Consequently, breathing becomes easier and recovery accelerates.
Moreover, physiotherapy improves chest expansion, strengthens respiratory muscles, and prevents complications such as pneumonia. Thus, it is an essential part of holistic bronchitis care.
Physiotherapy Goals in Bronchitis
From a physiotherapy perspective, treatment is goal-oriented. Specifically, the main objectives include:
- Clearing bronchial secretions
- Reducing breathlessness
- Improving ventilation
- Enhancing oxygen saturation
- Preventing lung stiffness
- Increasing exercise tolerance
Therefore, physiotherapy does not replace medicine but complements medical treatment effectively.
Chest Physiotherapy Techniques for Bronchitis
1. Postural Drainage
Postural drainage uses gravity to help drain mucus from different lung segments. By positioning the patient correctly, secretions move toward the larger airways. As a result, coughing becomes more effective.
This technique is especially useful in chronic bronchitis and bedridden patients. However, it should always be guided by a trained physiotherapist.
2. Percussion and Vibration
Bronchitis: Causes Symptoms Chest percussion involves rhythmic clapping over the chest wall. Meanwhile, vibration is applied during exhalation. Together, these techniques loosen thick mucus.
Consequently, mucus clearance improves significantly. Therefore, breathing effort reduces and lung sounds improve.
3. Controlled Coughing and Huffing
Effective coughing is essential in bronchitis. Physiotherapists teach controlled coughing techniques that clear mucus without exhausting the patient.
Huffing, on the other hand, is a forced exhalation without closing the throat. Thus, it helps move secretions from smaller airways safely.
Breathing Exercises in Bronchitis
Breathing exercises are a core component of physiotherapy treatment. They retrain breathing patterns and reduce respiratory distress.
1. Diaphragmatic Breathing
Diaphragmatic breathing encourages deep, efficient breaths. Instead of using chest muscles, the diaphragm does most of the work.
As a result:
- Oxygen intake increases
- Breathing effort decreases
- Anxiety reduces
Therefore, it is highly beneficial in both acute and chronic bronchitis.
2. Pursed Lip Breathing
Pursed lip breathing slows down exhalation. Consequently, air trapping reduces and breathlessness improves.
This technique is particularly useful in chronic bronchitis patients with wheezing.
3. Segmental Breathing
Segmental breathing improves expansion of specific lung areas. By applying manual cues, the physiotherapist enhances localized ventilation.
Thus, lung compliance improves gradually.
Airway Clearance Devices
In modern physiotherapy, airway clearance devices are often used. These tools assist patients who struggle with manual techniques.
Examples include:
- Incentive spirometer
- Positive expiratory pressure (PEP) devices
Therefore, home-based physiotherapy becomes easier and more effective.
Exercise Therapy in Bronchitis
Once acute symptoms subside, exercise therapy becomes important. Regular physical activity improves lung endurance and overall health.
Recommended Exercises
- Walking
- Low-intensity cycling
- Upper limb mobility exercises
- Breathing-coordinated movements
However, exercise intensity must be gradual. Otherwise, breathlessness may increase.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation for Chronic Bronchitis
Bronchitis: Causes Symptoms Pulmonary rehabilitation is a structured physiotherapy program. It combines exercise training, breathing techniques, and education.
Benefits include:
- Improved quality of life
- Reduced hospital admissions
- Better symptom control
- Increased independence
Thus, pulmonary rehabilitation is strongly recommended for chronic bronchitis patients.
Physiotherapy in Acute vs Chronic Bronchitis
| Aspect | Acute Bronchitis | Chronic Bronchitis |
| Focus | Symptom relief | Long-term management |
| Techniques | Breathing + positioning | Airway clearance + rehab |
| Duration | Short-term | Ongoing |
| Goal | Recovery | Disease control |
Therefore, treatment plans are always individualized.
Precautions During Physiotherapy
Although physiotherapy is safe, precautions are essential.
Physiotherapy should be avoided or modified if:
- High fever is present
- Severe chest pain occurs
- Oxygen levels are unstable
- Active hemoptysis exists
Hence, coordination with a physician is necessary.
Home-Based Physiotherapy Advice
Physiotherapists also guide patients for home care. This ensures continuity of treatment.
Home advice includes:
- Daily breathing exercises
- Adequate hydration
- Proper coughing techniques
- Correct posture
- Avoiding smoke and pollutants
As a result, recovery becomes faster and relapse reduces.
Role of Physiotherapist in Bronchitis Management
A physiotherapist acts as:
- Airway clearance specialist
- Breathing trainer
- Exercise guide
- Patient educator
Therefore, physiotherapy bridges the gap between medicine and functional recovery.
FAQs – Physiotherapy Treatment in Bronchitis
Is physiotherapy necessary for bronchitis?
Yes, especially in chronic or recurrent bronchitis, physiotherapy significantly improves outcomes.
Can physiotherapy reduce cough in bronchitis?
Yes, by clearing mucus and improving breathing efficiency.
Is chest physiotherapy painful?
No, when done correctly, it is safe and comfortable.
How long is physiotherapy needed?
Acute cases may need a few sessions, whereas chronic bronchitis requires long-term management.
Can physiotherapy prevent bronchitis complications?
Yes, it reduces the risk of pneumonia and lung damage.
Conclusion (Physio Perspective)
Bronchitis: Causes Symptoms From a physiotherapy perspective, bronchitis management goes beyond medication. By improving airway clearance, breathing mechanics, and physical capacity, physiotherapy plays a vital role in recovery and prevention.
Therefore, integrating physiotherapy into bronchitis treatment ensures better lung health, faster recovery, and improved quality of life.