Overview
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among men worldwide. As medical research advances, the demand for accurate, affordable, and fast diagnostic methods continues to grow. Traditionally, prostate cancer detection has relied heavily on lengthy MRI scans, invasive biopsies, and costly tests. However, a new breakthrough offers a promising alternative. Researchers have developed a shortened MRI protocol that makes prostate cancer detection faster, cheaper, and more accessible without compromising accuracy.
In this blog post, we will explore how this advancement is changing the landscape of cancer diagnosis, why it matters, and what it means for patients globally.
Why Prostate Cancer Detection Matters
Prostate cancer detection is crucial because early diagnosis often leads to better treatment outcomes. However, many men avoid screening due to fears of discomfort, high costs, or lack of access to advanced imaging technology. Therefore, healthcare providers have long sought ways to make screening both effective and practical.
Consequently, traditional MRI scans—although accurate—come with significant drawbacks. These scans can take up to 45 minutes, require highly trained technicians, and consume large amounts of hospital resources. As a result, many patients either face delays or skip screening altogether. Hence, the need for an efficient and reliable method has never been greater.
The Breakthrough: Shortened MRI for Prostate Cancer Detection
Recently, researchers across 22 hospitals in 12 countries tested a shorter MRI protocol. This method reduces scanning time from nearly 45 minutes to just 15–20 minutes. Importantly, the results revealed that shorter MRIs detected prostate cancer with nearly the same accuracy as traditional methods.
Therefore, shortened MRIs not only save time but also lower costs significantly. Because the shorter scans require fewer hospital resources, more patients can undergo prostate cancer detection in a single day. Moreover, the quicker process helps reduce patient anxiety and improves overall comfort.
How the Shortened MRI Works
Although the technology may sound complex, the process is straightforward. Traditionally, an MRI for prostate cancer detection includes several sequences, which together build a detailed picture of the prostate. In contrast, the shortened MRI focuses only on the most critical imaging sequences.
As a result, the procedure captures the essential diagnostic information without unnecessary repetition. Thus, the patient spends less time inside the MRI machine while still receiving accurate results. Furthermore, because technicians can perform more scans in a shorter period, hospitals can serve more patients without increasing costs.
Benefits of Shortened MRI for Prostate Cancer Detection
1. Faster Results
Since the scans are shorter, patients spend less time waiting for appointments. Consequently, doctors can provide diagnoses more quickly, enabling earlier treatment.
2. Lower Costs
Because shorter MRIs use fewer resources, the overall cost per scan decreases. Therefore, this makes prostate cancer detection more affordable for patients and healthcare systems alike.
3. Increased Accessibility
Shorter scans free up MRI machines, allowing hospitals to screen more patients each day. As a result, accessibility improves, especially in regions where advanced medical equipment is limited.
4. Greater Patient Comfort
Long MRI sessions can be stressful, particularly for patients who feel claustrophobic. However, shortened MRIs significantly reduce discomfort and anxiety, encouraging more men to undergo prostate cancer detection.
5. Comparable Accuracy
Most importantly, the accuracy of shortened MRIs remains nearly identical to traditional methods. Therefore, patients can trust that they are receiving reliable results without unnecessary delays or expenses.
Global Impact of Shortened MRI Research
The findings from this international study hold major implications worldwide. In high-income countries, shortened MRIs could reduce healthcare costs and streamline cancer detection. In developing nations, where access to medical imaging is often limited, this advancement could make prostate cancer detection available to a much larger population.
Furthermore, since prostate cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men, improving detection methods could save thousands of lives annually. Thus, the global impact of this breakthrough cannot be overstated.
Challenges Ahead
Although the research is promising, some challenges remain. For example, not all hospitals currently have access to MRI machines capable of running the shortened protocol. Moreover, radiologists and technicians must be trained to adapt to the new process.
Additionally, while the shortened MRI has shown strong accuracy, larger clinical trials may be needed to confirm its effectiveness across different populations. Nevertheless, these challenges are manageable, and the potential benefits far outweigh the obstacles.
Future of Prostate Cancer Detection
As technology evolves, prostate cancer detection will continue to improve. In the near future, we may see even more advanced imaging methods powered by artificial intelligence. AI could analyze MRI scans automatically, helping doctors identify cancer with even greater precision.
Moreover, combining shortened MRI with blood tests, genetic screening, and AI tools could create a powerful, multi-layered approach to prostate cancer detection. Therefore, the future looks bright for both patients and healthcare providers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, shortened MRI scans represent a game-changing development in prostate cancer detection. They are faster, cheaper, more comfortable, and just as accurate as traditional methods. As healthcare systems worldwide adopt this innovation, millions of men could benefit from earlier, more accessible screening. Because early detection saves lives, this breakthrough offers hope for reducing the global burden of prostate cancer. Therefore, adopting shortened MRI protocols is not only a scientific achievement but also a vital step forward for public health.
-
Bachelor of Physiotherapy: Complete Career Guide for Future Physiotherapists

Bachelor of Physiotherapy Bachelor of Physiotherapy: Firstly, healthcare is one of the fastest-growing sectors in India and across the world. …
-
Bachelor in Physiotherapy: Complete Career Guide for Future Physiotherapists

Bachelor in Physiotherapy Bachelor of Physiotherapy: Firstly, healthcare is one of the fastest-growing sectors in India and across the world. …
-
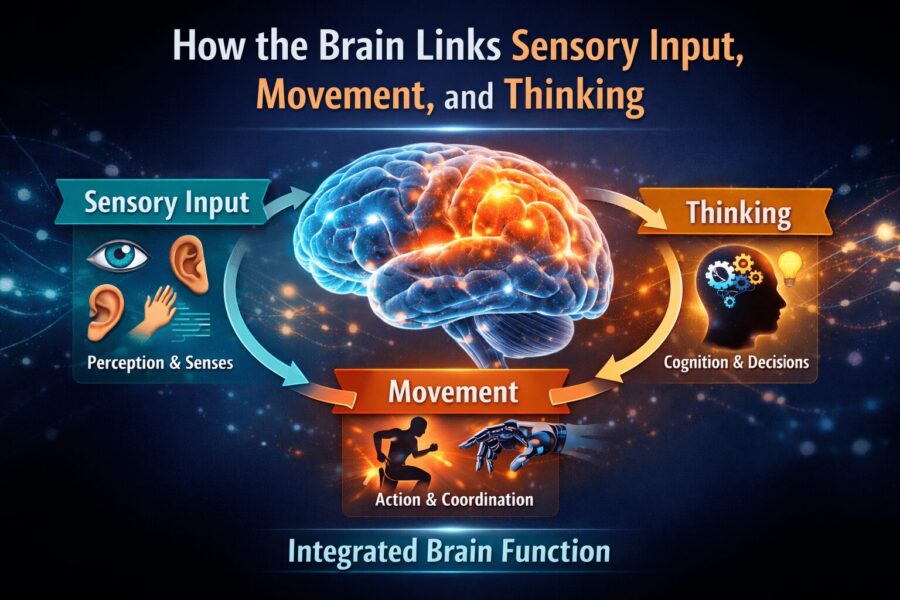
How the Brain Links Sensory Input, Movement, and Thinking

Author Bio: Dr. Ram Prakasha BPThWritten by a Physiotherapy and Public Health professional with experience in neurological rehabilitation and health awareness. …
FAQs About Prostate Cancer Detection
1. What is prostate cancer detection?
Prostate cancer detection refers to the process of identifying cancer in the prostate gland, usually through blood tests, MRI scans, and sometimes biopsies.
2. How does a shortened MRI help in prostate cancer detection?
A shortened MRI uses fewer imaging sequences, reducing scan time to 15–20 minutes while maintaining high accuracy in detecting prostate cancer.
3. Is a shortened MRI as accurate as a traditional MRI?
Yes. Research shows that shortened MRIs detect prostate cancer with nearly the same accuracy as traditional scans, making them a reliable alternative.
4. Does a shortened MRI cost less than a traditional MRI?
Yes. Because the scan takes less time and requires fewer hospital resources, it is generally more affordable for patients.
5. Who should get prostate cancer detection?
Men over 50, or those with a family history of prostate cancer, should discuss screening options with their doctors. Early detection often leads to better treatment outcomes.
6. Will shortened MRI replace traditional MRI completely?
Not immediately. While shortened MRIs are highly effective, traditional MRIs may still be used in complex cases. However, shortened MRIs will likely become a common first-line tool.
7. Is the shortened MRI available everywhere?
Currently, it is being adopted gradually. Availability may depend on hospital resources, but the method is expected to spread globally in the coming years.
References
- Giganti, F., et al. (2025). Abbreviated MRI protocols for prostate cancer detection: results from a multicenter international trial. European Urology.
- The Financial Times. (2025, September 11). Prostate cancers can be detected with shorter, cheaper scans, study shows. Retrieved from FT.com
- The Guardian. (2025, September 5). Gamechanger new findings on tackling heart conditions and prostate cancer detection. Retrieved from TheGuardian.com
- American Cancer Society. (2025). Prostate Cancer Early Detection. Retrieved from cancer.org
- National Cancer Institute. (2025). Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test and Imaging in Prostate Cancer Detection. Retrieved from cancer.gov